
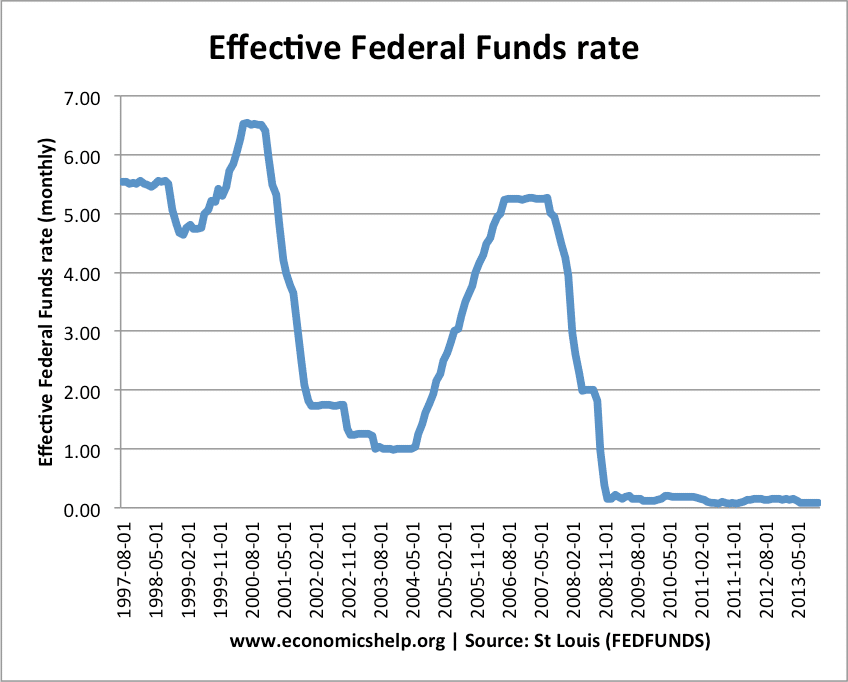
The world currency market is so large, however, that intervention does not affect exchange rates for long. Exchange market intervention occurs when governments buy and sell currencies to prevent changes in the exchange rate.Although this rule would keep inflation low in the long run, central banks and most economists feel that money demand moves around too much for such a rule to work well in practice. A constant money growth rule is simply to keep the growth rate of the money supply fixed from year to year.The Fed and other central banks respond to the gap, or the difference, between real GDP and potential GDP, as well as to inflation, in this way. When the economy goes into a recession, so that real GDP falls below potential GDP, the Fed lowers interest rates, stimulating investment and net exports and leading to a quicker recovery. When the economy enters a boom, so that real GDP exceeds potential GDP, the Fed raises the interest rate even if inflation has not yet started to increase. This form of a monetary policy rule is called the Taylor rule. Along with reacting to inflation, the Fed raises the interest rate when real GDP rises above potential GDP and lowers the interest rate when real GDP falls below potential GDP. Including real GDP in the monetary policy rule is a slight modification of this rule. In Chapter 24, we studied a monetary policy rule in which the Fed increases the real interest rate when inflation rises and decreases the interest rate when inflation falls and used the rule to derive a downward-sloping aggregate demand ( AD) curve.Changes in the discount rate always receive a lot of publicity, and the Fed sometimes changes the discount rate when it wants to bring public attention to its actions or provide a signal of its future intentions. The ability to borrow from the Fed increases people’s confidence in the safety of their bank deposits, and the Fed is called the lender of the last resort. The discount rate is the rate that commercial banks are charged when they borrow from the Fed.The federal funds rate is closely related to the longer-term interest rates on Treasury bills and certificates of deposit, which are relevant for money demand. It is the short-term interest rate that banks charge one another on overnight loans. The federal funds rate is the interest rate that the Fed looks at to make sure its actions have the intended effect. When the Fed wants to raise the interest rate, it sells bonds, decreasing the money supply. When the Fed wants to lower the interest rate, it buys bonds, increasing the money supply.

The interest rate is determined by the demand for money and the supply of money.When the interest rates on the alternatives fall, the opportunity cost decreases and money demand rises. When the interest rates on the alternatives to holding money rise, the opportunity cost increases and money demand falls. The opportunity cost of holding money is the interest rate on the alternatives minus the interest paid on checking accounts for deposits. Alternatives, such as certificates of deposit and Treasury bills, pay higher interest rates. Currency pays no interest, while checking accounts pay relatively low interest. Money is only part of most individuals’ wealth. Money demand is defined as a relationship between the interest rate and the amount of money that people want to hold at that interest rate.The most important feature of a central bank is central bank independence, the degree of independence the law gives it from the government. The central bank-the Federal Reserve System (Fed) in the United States, the European Central Bank, and the Bank of Japan-is responsible for monetary policy in most countries. Monetary policy is the set of actions taken by the government that affect the money supply and thereby interest rates, exchange rates, inflation, unemployment, and real GDP.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
